When playing sport or spending time under a tensile membrane roof or shade structure, you might wonder how effective these fabric structures are at protecting you from harmful sun exposure. While terms like SPF (Sun Protection Factor) are well-known to the general public, measuring sun protection for tensile membranes involves a different approach. Instead, we look at Ultraviolet Effectiveness (% UVE), which indicates how much UV radiation is effectively blocked by the material.
Below is a brief overview into the science of shade materials like PTFE, PVC, and HDPE, exploring their UVE properties and what it means for your safety.
What is UV Radiation
The light from the sun can be measured and classified in various wavelengths. When we talk about sun protection, we are essentially talking about protection against the non-visible ultraviolet waves (UV). UV radiation is divided into three categories:
- UVA (315–400 nm): UVA waves transmit freely through the earth atmosphere. UVA penetrates deeper into the skin, contributing to ageing and long-term damage.
- UVB (280–315 nm): Only about 15% of UVB transmits through the earth’s atmosphere, the rest is absorbed by the ozone layer. UVB is still the main cause of sunburn and plays a major role in the development of skin cancer.
- UVC (100–280 nm): Mostly absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere and not a concern under natural sunlight.
What Is the Difference between SPF and UVE?
Most of us are familiar with the term SPF (Sun Protection Factor). SPF is a measurement used for sunscreens to indicate how well they protect against UVB rays, the primary cause of sunburn. An SPF of 30, for example, means it would take 30 times longer for your skin to redden compared to being unprotected. Unlike lotions or creams, tensile membrane materials do not use SPF ratings because they operate differently by physically blocking or filtering UV radiation.
However, tensile membranes can be given an ultraviolet effectiveness percentage (% UVE), which measures their effectiveness in blocking ultraviolet radiation directly. Architectural fabrics used in engineered shade structures, such as PVC, PTFE, and HDPE Shade Mesh are effective sun protection materials because they allow some visible light to pass through, creating a bright and airy environment, while simultaneously offering high UVE to ensure sun safety.
Why UVE Matters
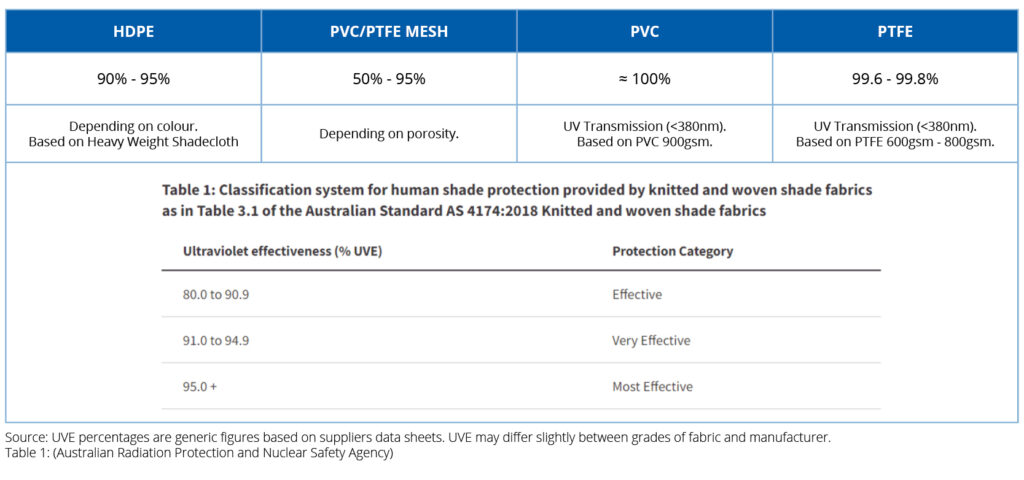
Ultraviolet Effectiveness measures the percentage of UV radiation blocked by a material. For tensile membranes, the majority of UV that passes through falls within the visible light spectrum, which poses far less risk to human health. High UVE ratings indicate significant protection against the harmful effects of UV radiation, including sunburn, premature ageing, and skin cancer. According to ARPANSA (Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency); “Any fabric providing protection from the sun, sky and reflections, that has a rating of 97% UVE or above can provide all day protection from solar UVR.”
UVE Ratings for PTFE, PVC, and HDPE
- PTFE Membranes: The most highly translucent of the solid fabrics we use, PTFE allows up to 15% visible natural light to pass through. Laboratory testing also confirms that PTFE fabric achieves over 99% UVE, effectively blocking nearly all harmful UVA and UVB radiation. The bright, white surface of PTFE means its reflective properties enhances its UV-blocking performance, ensuring excellent protection against harmful radiation.
- PVC Membranes: High-quality PVC membranes also provide excellent sun protection, with UVE ratings exceeding 99%+. Many PVC fabrics are treated with UV inhibitors, which slow their degradation over time under the harsh Australian sunlight. These UV treatments work by absorbing or reflecting UV radiation, thereby minimising both material wear and the transmission of harmful rays. These UV treatments help to enhance their ability to block harmful radiation over the lifespan of the structure, which can exceed 15-20 years with proper maintenance
- HDPE Shade Mesh: The UVE performance of HDPE shade mesh varies based on its colour and density. Darker colours and tighter weaves generally achieve higher UVE ratings, ranging from 90% to 95%. This versatility allows designers to optimise protection while maintaining aesthetic appeal. The knitted structure of HDPE promotes airflow, making it a popular choice for hot climates.
Real-World Performance
In Australia, where UV levels can reach extreme ratings, tensile membrane roofs provide a safe and comfortable environment. For example, a PTFE canopy over a sports facility or public space blocks nearly all harmful UV radiation while allowing diffused natural light to illuminate the area. Similarly, HDPE shade sails are widely used in playgrounds, schools, and outdoor recreation areas for their ability to provide effective UV protection and aesthetic versatility. This combination of protection and functionality underscores why tensile membranes are a preferred choice for outdoor shade structures.

Additional Sun Safety Tips
Although tensile membranes provide exceptional sun protection, it’s important to remember that UV exposure can still occur from indirect sources such as reflected sunlight, including surfaces like water, sand, or even of the windows of nearby parked cars. For those in high-risk categories, such as individuals with fair skin or a history of skin cancer, taking additional precautions is advisable:
- Wear a Hat and Sunglasses: Protect your face and eyes from reflected light.
- Apply Sunscreen: Use broad-spectrum sunscreen on exposed skin for extended periods outdoors.
- Stay Hydrated: Despite offering amazing protection against the sun, tensile membrane shade structures and roofs are still considered outdoor structures, on really hot days, the heat under any structure can still affect your comfort and health – you should still be drinking plenty of water.
Research and Further Reading
For more information about UV protection and tensile materials, consider exploring these resources:
- “Sun Protection Using Shade” by ARPANSA
https://www.arpansa.gov.au/understanding-radiation/radiation-sources/more-radiation-sources/sun-protection-shade
- “Sun Safety” by Cancer Council Australia
https://www.cancer.org.au/cancer-information/causes-and-prevention/sun-safety
By understanding the science behind tensile membranes, you can enjoy outdoor activities with confidence, knowing you’re well-protected from the sun’s harmful effects.

