When assessing the sustainability of architectural fabric structures, there are four key areas that MakMax addresses;

- the manufacturing process,
- overall embodied carbon of a structure,
- the lifecycle assessment of a structure and
- the use of materials that can be recycled at the end of their usable life.
MANUFACTURING
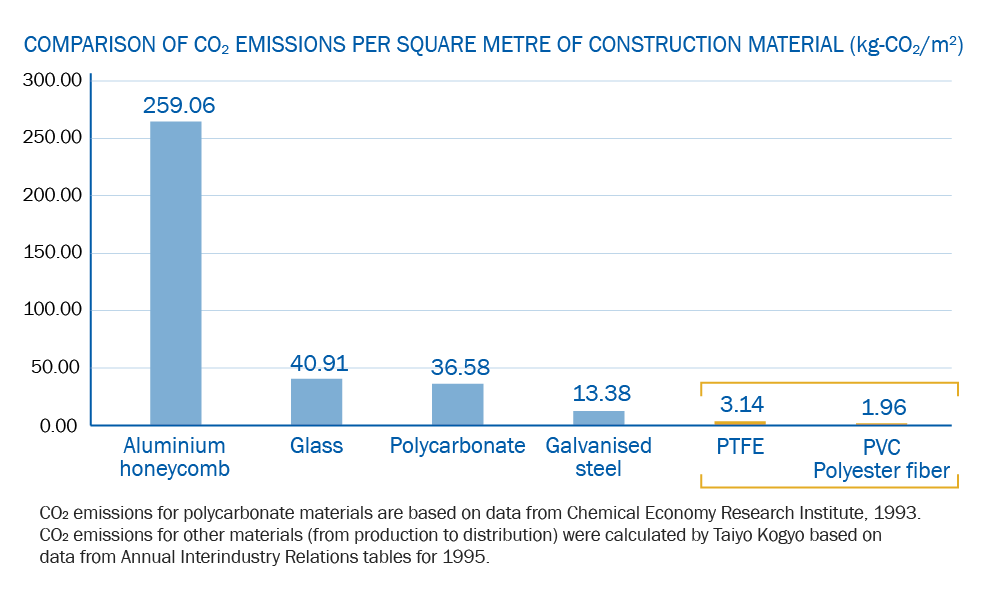
The environmental advantages of tensile membrane materials become evident when considering the significantly lower carbon footprint associated with their manufacturing process in comparison to similar roofing materials. The production of a square metre of tensile membrane material produces a substantially reduced emission of carbon dioxide (CO2) compared to alternative roofing materials.
This notable reduction in CO2 emissions can be attributed to several factors inherent to the manufacturing of tensile membrane materials. The lightweight nature of these materials requires fewer raw resources, leading to decreased energy consumption in extraction, transportation, and processing. Additionally, the manufacturing techniques employed in creating tensile membrane materials often involve more efficient processes and utilize innovative technologies that contribute to a lower overall environmental impact.
A square metre of membrane material generates less CO2 emissions during the manufacturing process, compared to similar roofing materials (research study conducted by Taiyo Kogyo Japan).
Fabrics used on MakMax structures are premium architectural grade materials from approved suppliers with documented sustainable development goals. The materials chosen for tensile membranes often boast inherently eco-friendly properties, often coming with EPDs or PEET certification from the suppliers.
In essence, the environmental benefits of using tensile membrane materials extend beyond their performance in the built environment. By opting for these materials, one not only ensures structural efficiency but also aligns with a commitment to minimizing the ecological impact of construction processes, making a positive contribution to overall environmental stewardship and sustainability goals.
LOWER EMBODIED CARBON
Architectural fabrics, serving as exceptionally lightweight roofing or cladding materials, offer a range of benefits beyond their weight. Their unique characteristics allow for the use of lighter substructures, minimizing the need for extensive steelwork and concrete footings. This not only reduces the overall weight of the structure but also contributes to a more sustainable construction process.
The lightweight nature of architectural fabrics not only simplifies the support requirements but also enhances flexibility in design and installation. As a result, structures utilising these fabrics can achieve a significant reduction in building materials compared to conventional roofing materials like steel or glass. This reduction in materials translates to a substantial decrease in the embodied carbon cost associated with the construction of the structure.
By opting for architectural fabrics, architects and builders not only enhance the structural efficiency and design possibilities but also contribute to environmental sustainability by lessening the environmental impact of the construction process. This holistic approach aligns with the growing emphasis on eco-friendly and resource-efficient construction practices, making architectural fabrics a compelling choice for those seeking both performance and sustainability in their building projects.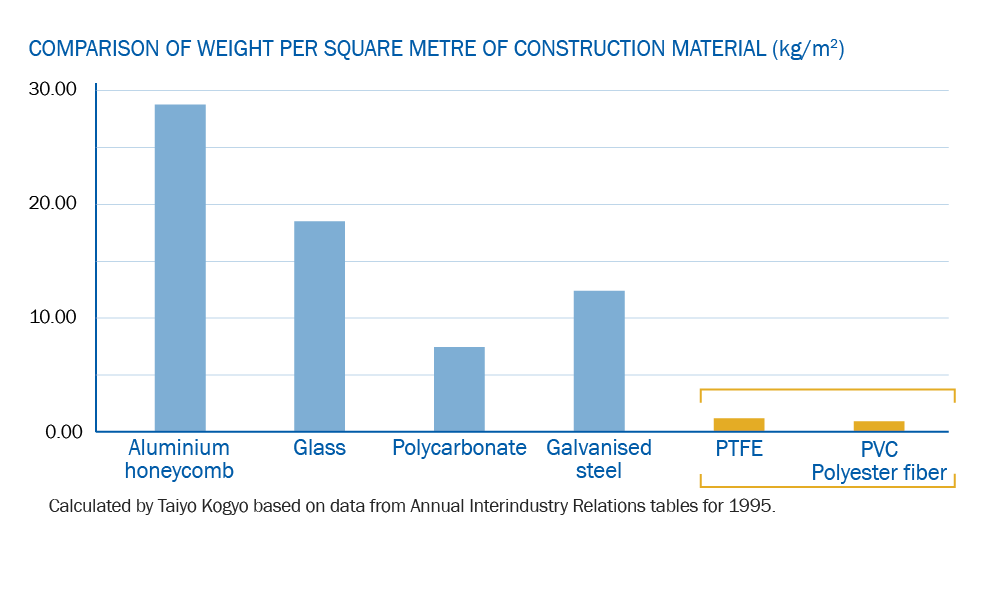
LIFE-CYCLE ASSESSMENT
MakMax fabric structures exemplify a commitment to sustainability through a comprehensive life-cycle assessment. Engineered for strength and longevity, these structures are designed to endure for up to 50 years. This extended lifespan not only underscores their durability but also plays a pivotal role in reducing the need for frequent repairs and material replacements over the course of the structure’s life cycle.
The resilience and lasting performance of MakMax fabric structures align with the principles of responsible construction and resource conservation. By minimizing the frequency of repairs and replacements, these structures contribute to a more sustainable approach to infrastructure development. This approach not only reduces the demand for additional raw materials but also lessens the associated energy and environmental costs of manufacturing and installing new components.
In addition to their durability, MakMax fabric structures incorporate advanced technology and design principles that enhance their environmental efficiency. Tensile membrane structures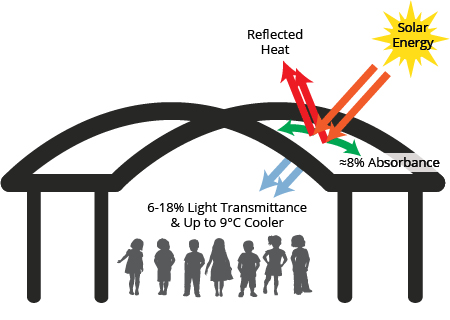 combine lightweight and translucent qualities with remarkably effective insulation properties. This minimises solar energy and heat infiltration into the structure while permitting the entry of natural light. Consequently, fabric roofing and cladding can yield highly energy-efficient structures, leading to cost and energy savings due to reduced requirements for cooling and lighting.
combine lightweight and translucent qualities with remarkably effective insulation properties. This minimises solar energy and heat infiltration into the structure while permitting the entry of natural light. Consequently, fabric roofing and cladding can yield highly energy-efficient structures, leading to cost and energy savings due to reduced requirements for cooling and lighting.
In essence, the integration of advanced materials and thoughtful design in MakMax fabric structures reflects a holistic commitment to sustainability across the entire life cycle. From initial construction through decades of use, these structures exemplify a harmonious balance between durability, energy efficiency, and responsible resource management, making them a prudent choice for environmentally conscious and forward-thinking construction projects.
FURTHER READNG: An article from the November 2023 Green Review talks about Cool Roofs reducing the energy required for cooling and mitigating the urban heat island effect. They describe Cool Roofs as characterised by high solar reflectance (which is one of the defining features of a tensile membrane canopy). READ THE ARTICLE HERE.
RECYCLABLE MATERIALS
An integral aspect of the commitment towards the sustainability of architectural fabrics is MakMax use of recyclable materials and a design that facilitates efficient disassembly in our structures. The components of these structures, including structural steel and hardware, are individually recyclable. At the conclusion of the structure’s lifespan, the steel components are directed to recycling plants, minimizing the environmental impact associated with the disposal of these materials.
Many of the fabrics used in MakMax structures are potentially recyclable, particularly single-material fabrics like HDPE and ETFE. The simplicity of these materials makes the recycling process straightforward, offering an environmentally conscious solution for the end of their usable life.
Due to the complexity of separating the base cloth from the protective coatings, composite fabrics, such as PVC present challenges in current recycling practices due to cost constraints. However,  MakMax actively collaborates with PVC fabric suppliers who champion recycling initiatives. Serge Ferrari’s Soltis Loop® is a new generation of innovative PVC products made of recycled materials, which embodies the companies sustainable approach: Aimed at saving natural resources, the Soltis Loop® ranges are a forerunner of tomorrow, when as an industry, we will be able do even more with less.
MakMax actively collaborates with PVC fabric suppliers who champion recycling initiatives. Serge Ferrari’s Soltis Loop® is a new generation of innovative PVC products made of recycled materials, which embodies the companies sustainable approach: Aimed at saving natural resources, the Soltis Loop® ranges are a forerunner of tomorrow, when as an industry, we will be able do even more with less.
We are also actively exploring new membrane materials, such as woven Polypropylene. PP membrane with similar tensile strength to PVC is being developed by a number of partner suppliers. Using the same polymer as the woven base cloth to the protective coating will make these new materials much easier to recycle at the end of their structural life.
By engaging in partnerships that support recycling programs, MakMax ensures that even materials with more complex recycling requirements contribute to a circular economy, aligning with broader sustainability goals.
As part of the global Taiyo Kogyo Group, we are committed to the research and development of new materials, technologies, processes and initiatives that align with our sustainability goals.
MakMax Australia believes that operating in a sustainable, responsible manner is an important business practice. We are conscious of our responsibility to the environment and ensure our people are engaged with our environmental protection processes.
We are committed to continually improving our systems and performance and our environmental management system is certified to ISO 14001.

